Research
Nucleus-aware Self-supervised Pretraining Using Unpaired Image-to-image Translation for Histopathology Images
- Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2023;
- Projects are available at https://github.com/zhiyuns/UNITPathSSL.
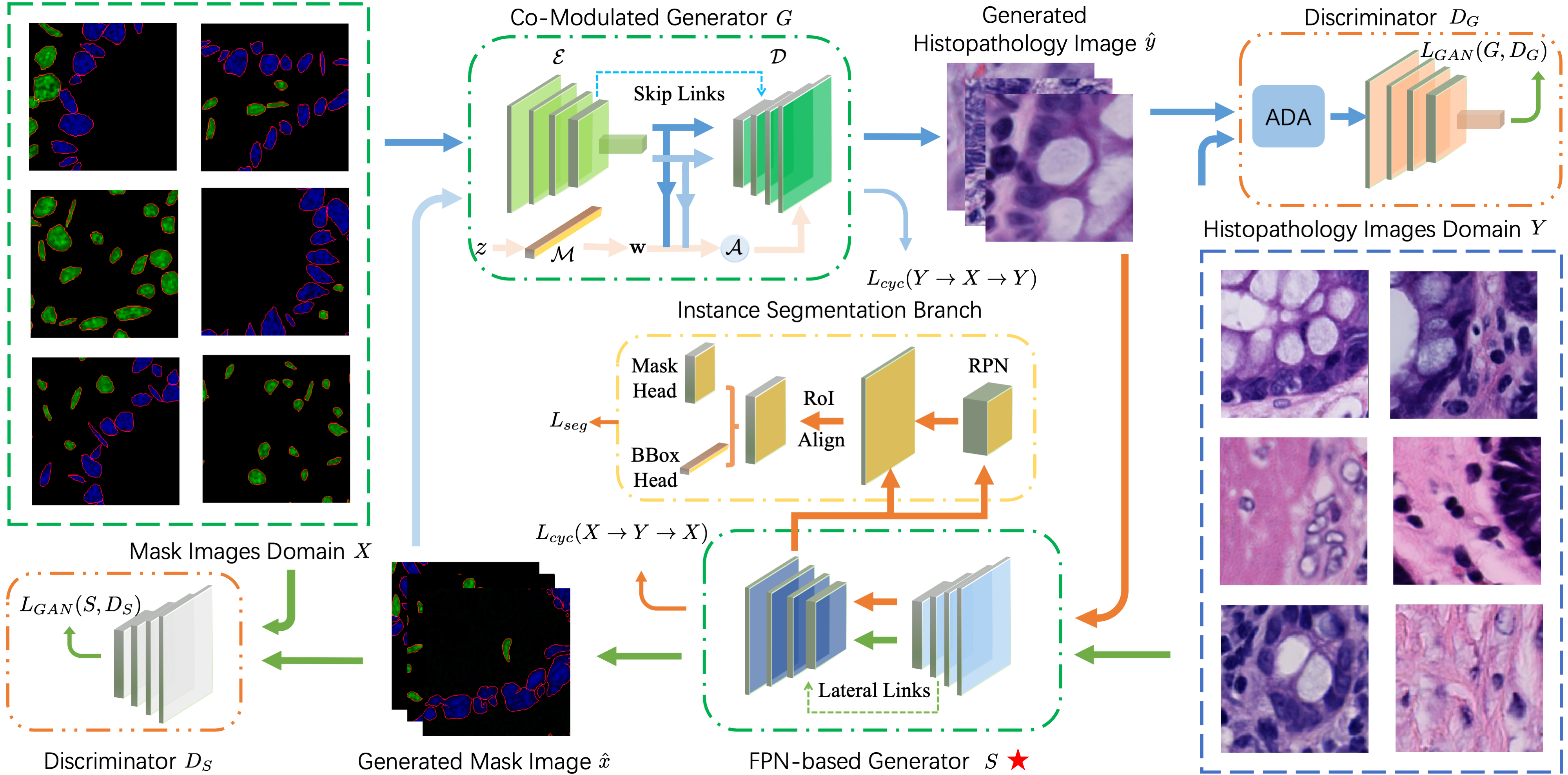
Self-supervised pretraining attempts to enhance model performance by obtaining effective features from unlabeled data, and has demonstrated its effectiveness in the field of histopathology images. Despite its success, few works concentrate on the extraction of nucleus-level information, which is essential for pathologic analysis. In this work, we propose a novel nucleus-aware self-supervised pretraining framework for histopathology images. The framework aims to capture the nuclear morphology and distribution information through unpaired image-to-image translation between histopathology images and pseudo mask images. The generation process is modulated by both conditional and stochastic style representations, ensuring the reality and diversity of the generated histopathology images for pretraining. Further, an instance segmentation guided strategy is employed to capture instance-level information. The experiments on 7 datasets show that the proposed pretraining method outperforms supervised ones on Kather classification, multiple instance learning, and 5 dense-prediction tasks with the transfer learning protocol, and yields superior results than other self-supervised approaches on 8 semi-supervised tasks.
Alias-Free Co-modulated Network for Cross-modality Synthesis and Super-resolution of MR Images
- Accepted by Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), 2023;
- Codes are available at https://github.com/zhiyuns/AFCM.
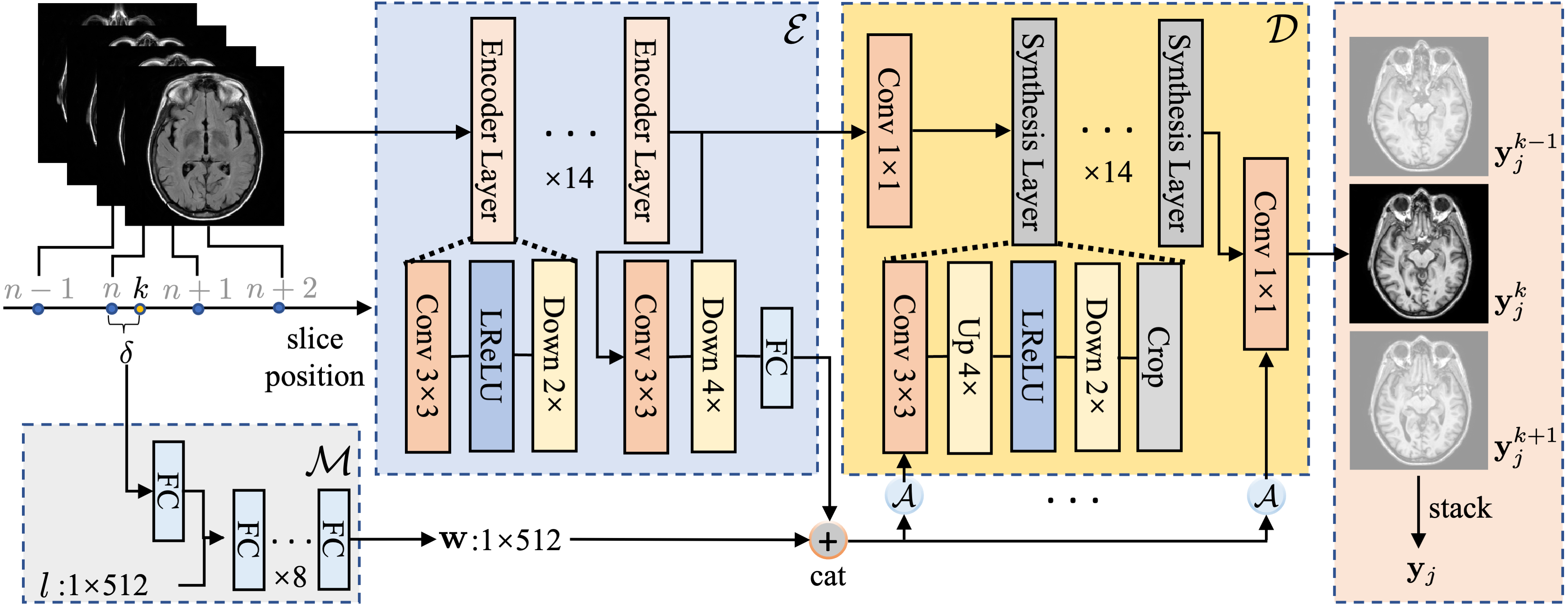
Cross-modality synthesis (CMS) and super-resolution (SR) have both been extensively studied with learning-based methods, which aim to synthesize desired modality images and reduce slice thickness for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), respectively. It is also desirable to build a network for simultaneous cross-modality and super-resolution (CMSR) so as to further bridge the gap between clinical scenarios and research studies. However, these works are limited to specific fields. None of them can flexibly adapt to various combinations of resolution and modality, and perform CMS, SR, and CMSR with a single network. Moreover, alias frequencies are often treated carelessly in these works, leading to inferior detail-restoration ability. In this paper, we propose Alias-Free Co-Modulated network (AFCM) to accomplish all the tasks with a single network design. To this end, we propose to perform CMS and SR consistently with co-modulation, which also provides the flexibility to reduce slice thickness to various, non-integer values for SR. Furthermore, the network is redesigned to be alias-free under the Shannon-Nyquist signal processing framework, ensuring efficient suppression of alias frequencies. Experiments on three datasets demonstrate that AFCM outperforms the alternatives in CMS, SR, and CMSR of MR images.
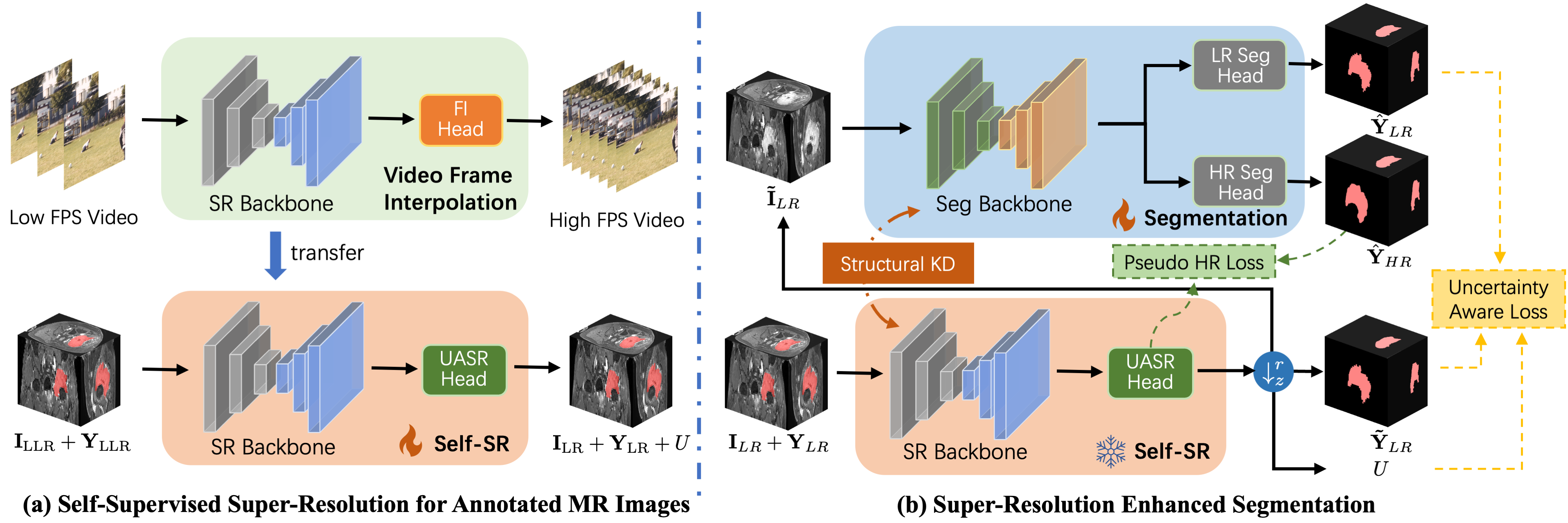
REHRSeg: Unleashing the Power of Self-supervised Super-resolution for Resource-efficient 3D MRI Segmentation
- Accepted by Neurocomputing, 2025;
- Codes are available at https://github.com/zhiyuns/REHRSeg.
High-resolution (HR) 3D magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide detailed anatomical structural information, enabling precise segmentation of regions of interest for various medical image analysis tasks. Due to the high demands of acquisition device, collection of HR images with their annotations is always impractical in clinical scenarios. Consequently, segmentation results based on low-resolution (LR) images with large slice thickness are often unsatisfactory for subsequent tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel Resource-Efficient High-Resolution Segmentation framework (REHRSeg) to address the above-mentioned challenges in real-world applications, which can achieve HR segmentation while only employing the LR images as input. REHRSeg is designed to leverage self-supervised super-resolution (self-SR) to provide pseudo supervision, therefore the relatively easier-to-acquire LR annotated images generated by 2D scanning protocols can be directly used for model training. The main contribution to ensure the effectiveness in self-SR for enhancing segmentation is three-fold: (1) We mitigate the data scarcity problem in the medical field by using pseudo-data for training the segmentation model. (2) We design an uncertainty-aware super-resolution (UASR) head in self-SR to raise the awareness of segmentation uncertainty as commonly appeared on the ROI boundaries. (3) We align the spatial features for self-SR and segmentation through structural knowledge distillation to enable a better capture of region correlations. Experimental results demonstrate that REHRSeg achieves high-quality HR segmentation without intensive supervision, while also significantly improving the baseline performance for LR segmentation.